Samacheer Kalvi students, hope you wrote your Chemistry exam well. Here is the Class XII Chemistry Exam Answer Key 2024 for your reference. If you need clarification for any answers, please let us know in the comments section.
Class XII Chemistry Exam Answer Key 2024
Part I
1. The rate constant of a reaction is 5.8 × 10-2 S-1 The order of the reaction is :
(a) Second order (b) First order
(c) Third order (d) Zero order
Answer: (b) First order
2. Aspirin is:
(a) chlorobenzoic acid (b) acetyl salicylic acid
(c) anthranilic acid (d) benzoyl salicylic acid
Answer: (b) acetyl salicylic acid
3. In acid medium, potassium permanganate oxidizes oxalic acid to:
(a) acetate (b) oxalate
(c) acetic acid (d) carbon dioxide
Answer: (d) carbon dioxide
4. IUPAC name of the complex K3[Al(C2O4)3] is:
(a) Potassium trisoxalato aluminate (III)
(b) Potassium trioxalato aluminium (III)
(c) Potassium trioxalato aluminate (III)
(d) Potassium trioxalato aluminate (II)
Answer: (c) Potassium trioxalato aluminate (III)
5. Among the following which will not be hydrolysed?
(a) Sodium Chloride (b) Sodium Formate
(c) Ammonium Formate (d) Ammonium Nitrate
Answer: (a) Sodium Chloride
6. Among the following cells primary cells are :
(i) Leclanche cell
(ii) Nickel-Cadmium cell
(iii) Lead Storage Battery
(iv) Mercury cell
(a) (iii) and (iv) (b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (iii)
Answer: (b) (i) and (iv)
7. In the electrolytic refining of copper, which one of the following is used as anode?
(a) Carbon rod (b) Pure copper
(c) Platinum electrode (d) Impure copper
Answer: (d) Impure copper
8. Assertion : Monoclinic sulphur is an example of monoclinic crystal system.
Reason: Fora monoclinic system, a ≠ b ≠ c and α= γ =90°, β ≠ 90°.
(a) Assertion is true but Reason is false.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Both Assertion and Reason are false.
(d) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
Answer: (b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
9. The formation of cyanohydrin from acetone is an example of :
(a) electrophilic addition (b) nucleophilic substitution
(c) nucleophilic addition (d) electrophilic substitution
Answer: (c) nucleophilic addition
10. Which of the following is not sp2 hybridised?
(a) Fullerene (b) Graphite
(c) Dry ice (d) Graphene
Answer: (c) Dry ice
11. The oxidizing agent used to stop the oxidation of primary alcohol at the aldehyde stage is :
(a) Na2,Cr2,O7, (b) KMnO4,
(c) K2 Cr2 O7 (d) PCC
Answer: (d) PCC
12. Which of the following is the strongest acid among all?
(a) HBr (b) HI
(c) HCl (d) HF
Answer: (b) HI
13. When aniline reacts with acetic anhydride, the product formed is :
(a) p-aminoacetophenone (b) o-aminoacetophenone
(c) acetanilide (d) m-aminoacetophenone
Answer: (c) acetanilide
14. The pyrimidine bases present in RNA are :
(a) Cytosine and Thiamine (b) Cytosine and Adenine
(c) Cytosine and Uracil (d) Cytosine and Guanine
Answer: (c) Cytosine and Uracil
15. Activity of iron catalyst is increased by the ____ compound.
(a) CH3COOH (b) H2S
(c) Al2 O3 (d) As2O3
Answer: (c) Al2 O3
Part II
16. What is calcination?
Calcination is the process in which the concentrated ore is strongly heated in the absence of air. During this process, the water of crystallisation present in the hydrated oxide escapes as moisture. Any organic matter (if present) also get expelled leaving behind a porous ore. For example, during calcination of carbonate ore, carbon dioxide is expelled.
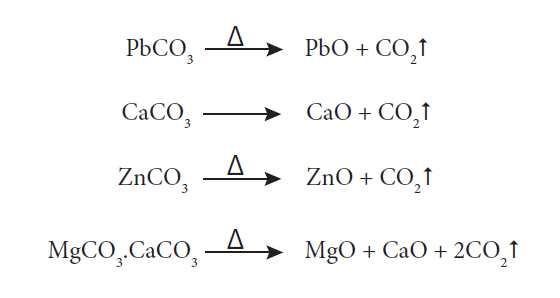
17. How will you convert boric acid to boron nitride?
Answer: Fusion of urea with B(OH)3, in an atmosphere of ammonia at 800 – 1200 K gives boron nitride.
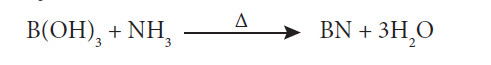
18. Give a reason to support that Sulphuric acid is a dehydrating agent. Justify with an example.
Answer: Sulphuric acid is highly soluble in water and has strong affinity towards it. Hence it can be used as a dehydrating agent. When dissolved in water, it forms mono (H2SO4.H2O) and dihydrates (H2SO4.2H2O) and the reaction is exothermic.
The dehydrating property can also be illustrated by its reaction with organic compounds such as sugar, oxalic acid and formic acid.
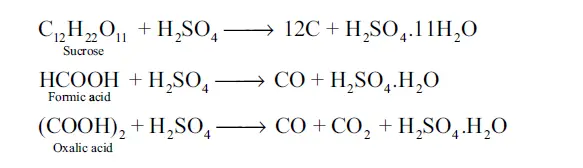
19. Explain common ion effect with an example.
Answer: When a salt of a weak acid is added to the acid itself, the dissociation of the weak acid is suppressed further. For example, the addition of sodium acetate to acetic acid solution leads to the suppression in the dissociation of acetic acid which is already weakly dissociated. In this case, ![]() and
and ![]() have the common ion,
have the common ion, ![]() .
.
Acetic acid is a weak acid. It is not completely dissociated in aqueous solution and hence the following equilibrium exists.
![]()
However, the added salt, sodium acetate, completely dissociates to produce ![]() and
and![]() ion.
ion.
![]()
20. Can ![]() oxidize bromide to bromine under standard conditions?
oxidize bromide to bromine under standard conditions?
Given: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Overall reaction:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is negative
is negative ![]() is positive and the cell reaction is non spontaneous.
is positive and the cell reaction is non spontaneous.
Hence ![]() cannot oxidise
cannot oxidise ![]()
21. Explain Kolbe’s reaction.
In Kolbe’s reaction, phenol is first converted into sodium phenoxide which is more reactive than phenol towards electrophilic substitution reaction with CO2 . Treatment of sodium phenoxide with CO2 at 400K, 4-7 bar pressure followed by acid hydrolysis gives salicylic acid.

22. Write the structure of ![]() glucopyranose and
glucopyranose and ![]() glucopyranose.
glucopyranose.
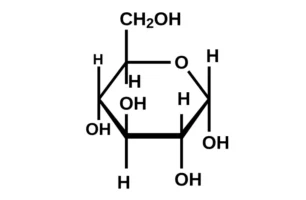
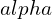 -D + glucopyranose
-D + glucopyranose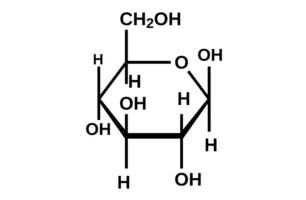
 -D + glucopyranose
-D + glucopyranose23. What are antibiotics?
Answer:
The medicines that have the ability to kill the pathogenic bacteria are grouped as antibiotics. Examples of antibiotic drugs include amoxicillin, ampicillin, and cefixime.
24. What is an order of a reaction?
Answer: Order of a reaction the sum of the powers of concentration terms involved in the experimentally determined rate law.
Part III
Answer any six of the following questions. Question No 33 is compulsory. [6×3=18]
25. Give the uses of helium.
- Helium and oxygen mixture is used by divers in place of air oxygen mixture. This prevents the painful dangerous condition called bends.
- Helium is used to provide inert atmosphere in electric arc welding of metals
- Helium has lowest boiling point hence used in cryogenics (low temperature science).
- It is much less denser than air and hence used for filling air balloons
26. Which is more stable? ![]() ? Explain.
? Explain.
Answer: Electronic Configuration: The electronic configuration of ![]() is [Ar]
is [Ar]![]() whereas the electronic configuration of
whereas the electronic configuration of ![]() is [Ar]
is [Ar]![]() .
.
Unpaired Electrons: ![]() has 5 unpaired electrons whereas
has 5 unpaired electrons whereas ![]() has 4 unpaired electrons.
has 4 unpaired electrons.
Subshells: ![]() has half filled
has half filled ![]() sub shell which is more stable compared to the partially filled d subshell of
sub shell which is more stable compared to the partially filled d subshell of ![]() .
.
Therefore, ![]() is more stable than
is more stable than ![]() .
.
27. Aluminium crystalizes in a cubic close packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125pm. Calculate the edge length of the cell unit.
Answer: r=125pm![]()
2×1.414×125
=353.5pm
Edge length of the cell is 353.5pm
28. Write Arrhenius equation and explain the terms involved.
Answer: ![]()
where A= frequency factor
R=gas constant
![]() =the activation energy
=the activation energy
T=the absolute temperature (in K)
29. Explain the effect of temperature and pressure on physisorption and chemisorption.
Answer: Effect of temperature: When temperature is raised chemisorption first increases and then decreases. whereas physisorption decreases with increase in temperature.
Effect of Pressure: In Chemical absorption is fast with increase in pressure, it can not alter the amount of
absorption. In Physisorption the extent of adsorption increases with increase in pressure.
30. Explain the Knoevenagal reaction.
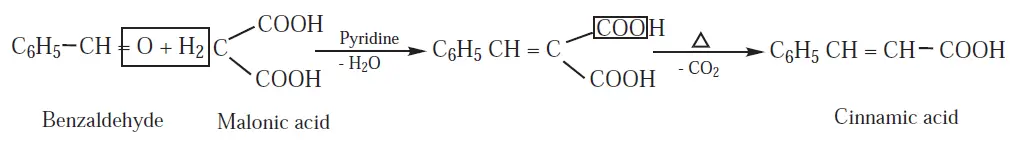
Benzaldehyde condenses with malonic acid in presence of pyridine forming cinnamic
acid, Pyridine act as the basic catalyst.
31. Write the reaction of primary amine with carbon disulphide ![]() .
.
Answer: When primary amines are treated with carbon disulphide ![]() , N – alkyldithio carbamic acid is formed which on subsequent treatment with
, N – alkyldithio carbamic acid is formed which on subsequent treatment with ![]() , gives an alkyl isothiocyanate.
, gives an alkyl isothiocyanate.

32. Write a short note on peptic bond.
Answer: The amino acids are linked covalently by peptide bonds. The carboxyl group of the first amino acid react with the amino group of the second amino acid to give an amide linkage between these amino acids. This amide linkage is called peptide bond.

33. In the complex, ![]() , identify the following.
, identify the following.
Answer: IUPAC Name: Dichloridodicyanido k-C Cobalt V chloride
Central metal ion: ![]()
Coordination number: 4
Part IV
Answer all the questions.
34. (a)(i). What are the differences between minerals and ores?
| Minerals | Ores |
| A naturally occurring substance obtained by mining which contains the metal in free state or in the form of compounds like oxides, sulphides etc… is called a mineral. | Minerals that contain a high percentage of metal, from which it can be extracted conveniently and economically are called ores. |
| All minerals are not ores | All ores are minerals |
| Bauxite and China clay are minerals of aluminium. | Bauxite is an ore of aluminium. |
34 (a) (ii) What is the role of silica in the extraction of copper?
Answer: In the extraction of copper from copper pyrites, the concentrated ore is heated in a reverberatory furnace after mixing with silica, which acts as an acidic flux. The ferrous oxide formed due to melting combines with silica to form ferrous silicate (slag).

34. (b)(i) Write the uses of boric acid.
Answer: Boric acid is used in the manufacture of eye drops, antiseptics, washing powders etc. It is also used in the manufacture of Pyrex glass. It is also used as a food preservative.
(a)(ii) What is silicate?
Answer: The mineral which contains silicon and oxygen in tetrahedral ![]() units linked together in different patterns are called silicates. Nearly 95 % of the earth crust is composed of silicate minerals and silica.
units linked together in different patterns are called silicates. Nearly 95 % of the earth crust is composed of silicate minerals and silica.
35 (a)(i) What is lanthanoid contraction and what are the effects of lanthanoid contraction?
Answer: As we move across the 4f series, the atomic and ionic radii of lanthanoids show gradual decrease with increase in atomic number. This decrease in ionic size is called lanthanoid contraction.
Effects of Lanthanoid contraction.
As we go from Ce3+ to Lu3+ , the basic character of Ln3+ ions decrease. Due to the decrease in the size of Ln3+ ions, the ionic character of Ln −OH bond decreases (covalent character increases) which results in the decrease in the basic nature.
In the complete f – series only 10 pm decrease in atomic radii and 20 pm decrease in ionic radii is observed. Because of this very small change in radii of lanthanoids, their chemical properties are quite similar.
The elements of the second and third transition series resemble each other more closely than the elements of the first and second transition series.
Example:
| Series | Element | Atomic Radius |
| 3d series | Ti | 132pm |
| 4d series | Zr | 145pm |
| 5d series | Hf | 144pm |
35. (b)(i) Write a short note on double salts and coordination compounds.
When two or more stable compounds in solution are mixed together and allowed to evaporate, in certain cases there is a possibility for the formation of double salts or coordination compounds. For example, when an equimolar solution of ferrous sulphate and ammonium sulphate are mixed and allowed to crystallize, a double salt namely Mohr’s salt (Ferrous ammonium sulphate, ![]() is formed.
is formed.
In the blood red colour formation in the inorganic qualitative analysis of ferric ion, the reaction between ferric chloride and potassium thiocyanate solution gives a blood red coloured coordination compound, potassium ferrithiocyanate ![]() .
.
If we perform a qualitative analysis to identify the constituent ions present in both the compounds, Mohr’s salt answers the presence of ![]() ions, whereas the potassium ferrithiocyanate will not answer
ions, whereas the potassium ferrithiocyanate will not answer ![]() and SCN-ions.
and SCN-ions.
From this we can infer that the double salts lose their identity and dissociates into their constituent simple ions in solutions , whereas the complex ion in coordination compound, does not lose its identity and never dissociates to give simple ions.
35. (b)(ii) Give an example of coordination compound used in medicine and two examples of biologically important coordination compounds.
Answer: Example of coordination compound in medicine:
- Ca-EDTA chelate, is used in the treatment of lead and radioactive poisoning. That is for removing lead and radioactive metal ions from the body.
Examples of biologically important coordination compounds:
- Vitamin B12(cyanocobalamine) is the only vitamin consisting of metal ion. it is a coordination complex in which the central metal ion is
 surrounded by Porphyrin like ligand.
surrounded by Porphyrin like ligand. - Many enzymes are known to be metal complexes; they regulate biological processes. For example, Carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that hydrolytic enzyme important in digestion, contains a zinc ion coordinated to the protein.
36.(a) Calculate the packing efficiency of sc unit cell.
Answer: a=2r
r=a/2
Volume of sphere with radius “r”
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
In a simple cubic arrangement, number of spheres belonging to a unit cell is equal to one.
Total volume occupied by the spheres in sc unit cell = 1x ![]()
Packing fraction = ![]()
![]()
=52.38%
36.(b) (i) Derive integrated rate law for a zero order reaction A![]() product.
product.
Answer: A reaction in which the rate is independent of the concentration of the reactant over a wide range of concentrations is called as zero order reactions. Such reactions are rare. Let us consider the following hypothetical zero order reaction.

36.(b) (ii) What is buffer index?
Answer: The buffering ability of a solution can be measured in terms of buffer capacity. Vanslyke introduced a quantity called buffer index, A ![]() , as a quantitative measure of the buffer capacity. It is defined as the number of gram equivalents of acid or base added to 1 litre of the buffer solution to change its pH by unity.
, as a quantitative measure of the buffer capacity. It is defined as the number of gram equivalents of acid or base added to 1 litre of the buffer solution to change its pH by unity.
A ![]()
Here, dB= number of gram equivalents of acid / base added to one litre of buffer solution.
d(pH) = The change in the pH after the addition of acid / base.
37.(a) (i) Write the cell terminology.
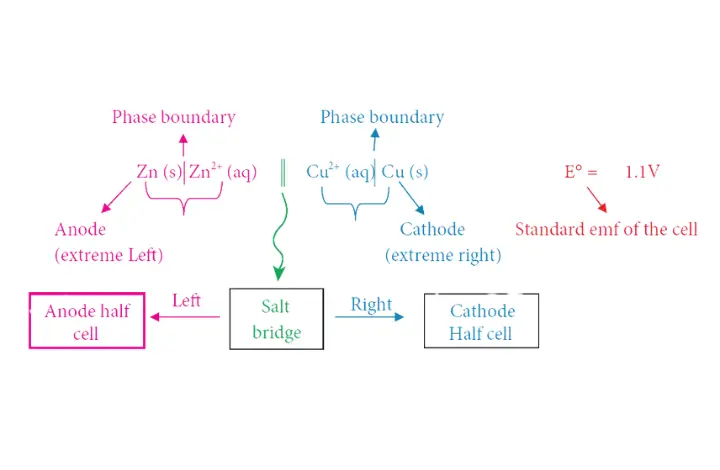
37. (a)(ii) Define Gold number.
Answer: Zsigmondy introduced the term ‘gold number’ as a measure of protecting power of a colloid. Gold number is defined as the number of milligrams of hydrophilic colloid that will just prevent the precipitation of 10ml of gold sol on the addition of 1ml of 10% NaCl solution. Smaller the gold number greater the protective power.
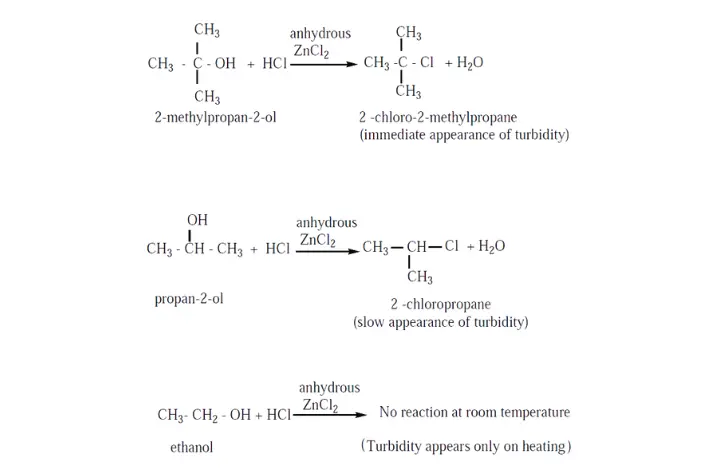
37. (b)(i) Write notes on Lucas test.
Answer: When alcohols are treated with Lucas agent (a mixture of concentrated HCl and anhydrous ![]() at room temperature, tertiary alcohols react immediately to form a turbidity due to the formation of alkyl chloride which is insoluble in the medium. Secondary alcohols react within 10 minutes to form a turbidity of alkyl chloride where primary alcohols do not react at room temperature.
at room temperature, tertiary alcohols react immediately to form a turbidity due to the formation of alkyl chloride which is insoluble in the medium. Secondary alcohols react within 10 minutes to form a turbidity of alkyl chloride where primary alcohols do not react at room temperature.
38. (a) (i) How acetic acid is prepared from Grignard reagent?
Answer: Grignard reagent reacts with carbondioxide (dry ice) to form salts of carboxylic acid which in turn give corresponding carboxylic acid after acidification with mineral acid.

38. (a) (ii) What are biodegradable polymers? Give examples.
Answer. The materials that are readily decomposed by microorganisms in the environment are called biodegradable. Natural polymers degrade on their own after certain period of time but the synthetic polymers do not. It leads to serious environmental pollution. One of the solution to this problem is to produce biodegradable polymers which can be broken down by soil micro organism.
Examples: Polyhydroxy butyrate (PHB) and Poly(3 hydroxy butyrate-co-3-hydroxy valerate) (PHBV)
38. (b) (i) An organic Compound (A) of molecular formula ![]() reacts with Zn-Hg / Conc. HCl to give Compound (B) which reacts with
reacts with Zn-Hg / Conc. HCl to give Compound (B) which reacts with ![]() forming Compound (C) (as major product) and Compound (D). Compound (C) reacts with conc. HCl to give Compound (E) (Table vinegar) and hydroxylamine. Identify A, B, C, D and E with suitable reactions.
forming Compound (C) (as major product) and Compound (D). Compound (C) reacts with conc. HCl to give Compound (E) (Table vinegar) and hydroxylamine. Identify A, B, C, D and E with suitable reactions.
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Compound | Molecular Formula | Name |
| A | Acetaldehyde | |
| B | Ethane | |
| C | Nitroethane | |
| D | Nitromethane | |
| E | Acetic Acid |
Leave a Reply