Part A – Multiple Choice Questions
| 1. The branches of the subject Economics is | |
| a) Wealth and welfare | |
| b) production and consumption | |
| c) Demand and supply | |
| d) micro and macro | |
| 2. Who coined the word ‘Macro’? | |
| a) Adam Smith | |
| b) J M Keynes | |
| c) Ragnar Frisch | |
| d) Karl Marx | |
| 3. Who is regarded as Father of Modern Macro Economics? | |
| a) Adam Smith | |
| b) J M Keynes | |
| c) Ragnar Frisch | |
| d) Karl Marx | |
| 4. Identify the other name for Macro Economics. | |
| a) Price Theory | |
| b) Income Theory | |
| c) Market Theory | |
| d) Micro Theory | |
| 5. Macro economics is a study of ___________________. | |
| a) individuals | |
| b) firms | |
| c) a nation | |
| d) aggregates | |
| 6. Indicate the contribution of J M Keynes to economics. | |
| a) Wealth of Nations | |
| b) General Theory | |
| c) Capital | |
| d) Public Finance | |
| 7. A steady increase in general price level is termed as_____________. | |
| a) wholesale price index | |
| b) Business Cycle | |
| c) Inflation | |
| d) National Income | |
| 8. Identify the necessity of Economic policies. | |
| a) to solve the basic problems | |
| b) to overcome the obstacles | |
| c) to achieve growth | |
| d) all the above | |
| 9. Indicate the fundamental economic activities of an economy. | |
| a) Production and Distribution | |
| b) Production and Exchange | |
| c) Production and Consumption | |
| d) Production and Marketing | |
| 10. An economy consists of | |
| a) consumption sector | |
| b) Production sector | |
| c) Government sector | |
| d) All the above | |
| 11. Identify the economic system where only private ownership of production exists. | |
| a) Capitalistic Economy | |
| b) Socialistic Economy | |
| c) Globalisic Economy | |
| d) Mixed Economy | |
| 12. Economic system representing equality in distribution is _________. | |
| a) Capitalism | |
| b) Globalism | |
| c) Mixedism | |
| d) Socialism | |
| 13. Who is referred as ‘Father of Capitalism’? | |
| a) Adam Smith | |
| b) Karl Marx | |
| c) Thackeray | |
| d) J M Keynes | |
| 14. The country following Capitalism is ________________ . | |
| a) Russia | |
| b) America | |
| c) India | |
| d) China | |
| 15. Identify The Father of Socialism. | |
| a) J M Keynes | |
| b) Karl Marx | |
| c) Adam Smith | |
| d) Samuelson | |
| 16. An economic system where the economic activities of a nation are done both by the private and public together is termed as_____________. | |
| a) Capitalistic Economy | |
| b) Socialistic Economy | |
| c) Globalisic Economy | |
| d) Mixed Economy | |
| 17. Quantity of a commodity accumulated at a point of time is termed as ____________.. | |
| a)production | |
| b) stock | |
| c) variable | |
| d) flow | |
| 18. Identify the flow variable. | |
| a) money supply | |
| b) assests | |
| c) income | |
| d) foreign exchange reserves | |
| 19. Identify the sectors of a Two Sector Model. | |
| a) Households and Firms | |
| b) Private and Public | |
| c) Internal and External | |
| d) Firms and Government | |
| 20. The Circular Flow Model that represents an open Economy. | |
| a) Two Sector Model | |
| b) Three Sector Model | |
| c) Four Sector Model | |
| d) All the above |
Part B – Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
21. Define Macro Economics.
Answer: The branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole is called Macro Economics. The word ‘Macro’ is derived from the Greek word ‘Makros’ meaning ‘large’. Macro Economics is the study of the economy as a whole. It deals with aggregates such as national income, employment and output. It is also known as ‘Income Theory’.
22. Define the term ‘Inflation’.
Answer: Inflation refers to steady increase in general price level. Estimating the general price level by constructing various price index numbers such as Wholesale Price Index, Consumer Price Index, etc, are needed.
23. What is meant by an ‘Economy’?
Answer: The term economy has been defined by A. J. Brown as, “A system by which people earn their living.” An economy is referred to any system or area where economic activities are carried out.
24. Classify the economies based on status of development.
Answer: Economies can be classified into different types based on the Status of Development as Developed, underdeveloped, undeveloped and developing economies.
25. What do you mean by Capitalism?
Answer: Capitalistic economy is also termed as a free economy (Laissez faire, in Latin) or market economy where the role of the government is minimum and market determines the economic activities.
26. Define ‘Economic Model’.
Answer: A model is a simplified representation of real situation. Economists use models to describe economic activities, their relationships and their behaviour.
27. ‘Circular Flow of Income’ – Define.
Answer: The circular flow of income is a model of an economy showing connections between different sectors of an economy. It shows flows of income, goods and services and factors of production between economic agents such as firms, households, government and nations.
Part – C : Answer the following questions in about a paragraph.
28. State the importance of Macro Economics.
Answer: The importance of macro economics are given below:
- Understanding the functioning of the economy at the aggregate level will help to evolve suitable strategies to solve the basic problems prevailing in an economy.
- Understanding the future problems, needs and challenges of an economy as a whole is important to evolve precautionary measures.
- It provides ample opportunities to use scientific investigation to understand the reality.
- It helps to make meaningful comparison and analysis of economic indicators.
- It helps for better prediction about future and to formulate suitable policies to avoid economic crises.
29. Describe the different types of economic systems.
Answer: Economic System refers to the manner in which individuals and institutions are connected together to carry out economic activities in a particular area. There are three major types of economic systems. They are:
- Capitalistic Economy (Capitalism),
- Socialistic Economy (Socialism)and
- Mixed Economy (Mixedism)
Capitalism and socialism are two extreme and opposite approaches. In capitalism, there is total freedom and private ownership of means of production. In socialism, there is no freedom for private and there is public ownership of means of production. Mixedism denotes the Co-existence of capitalism and socialism.
30. Outline the major merits of capitalism.
Answer: The major merits of capitalism are as follows:
- Automatic Working: Without any government intervention, the economy works automatically.
- Efficient Use of Resources: All resources are put into optimum use.
- Incentives for Hard work: Hard work is encouraged and entrepreneurs get more profit for more efficiency.
- Economic Progress: Production and productivity levels are very high in capitalistic economies.
- Consumers Sovereignty: All production activities are aimed at satisfying the consumers.
- Higher Rates of Capital Formation: Increase in saving and investment leads to higher rates of capital formation.
- Development of New Technology: As profit is aimed at, producers invest on new technology and produce quality goods.
31. Indicate the demerits of socialism.
Answer: The demerits of socialism are:
- Red Tapism and Bureaucracy: As decisions are taken by government agencies, approval of many officials and movement of files from one table to other takes time and leads to red tapism.
- Absence of Incentive: This system does not provide any incentive for efficiency. Therefore, productivity suffers.
- Limited Freedom of Choice: Consumers do not enjoy freedom of choice over the consumption of goods and services.
- Concentration of Power: The State takes all major decisions. The private takes no initiative in making economic decisions. Hence, the State is more powerful and misuse of power can also take place.
32. Enumerate the features of mixed economy.
Answer: The features of mixed economy are:
- Ownership of Property and Means of Production: The means of production and properties are owned by both private and public. Public and Private have the right to purchase, use or transfer their resources.
- Coexistence of Public and Private Sectors: In mixed economies, both private and public sectors coexist. Private industries undertake activities primarily for profit. Public sector firms are owned by the government with a view to maximize social welfare.
- Economic Planning: The central planning authority prepares the economic plans. National plans are drawn up by the Government and both private and public sectors abide. All sectors of the economy function according to the objectives,
priorities and targets laid down in the plan. - Solution to Economic Problems: The basic problems of what to produce, how
to produce, for whom to produce and how to distribute are solved through the price mechanism as well as state intervention. - Freedom and Control: Though private has freedom to own resources, produce
goods and services and distribute the same, the overall control on the economic activities rests with the government.
33. Distinguish between Capitalism and Globalism.
Answer:
| Features | Capitalism | Globalism |
| Definition | The system where the means of production are privately owned and market determines the economic activities. | An economic system where the economic activities of a nation are inter connected and inter dependent on each other nation. |
| Role of Government | The role of the government is minimum and market determines the economic activities. | Government’s role in globalisation involves establishing rules for international economic relationships, granting permissions for international operations, and managing impacts of globalisation on citizens. |
34. Briefly explain the two sector circular flow model.
Answer: There are only two sectors namely, household sector and firm sector.
(i) Household Sector: The household sector is the sole buyer of goods and services, and the sole supplier of factors of production, i.e., land, labour, capital and organisation. It spends its
entire income on the purchase of goods and services produced by the business sector. The household sector receives income from firm sector by providing the factors of production owned by it.
(ii) Firms: The firm sector generates its revenue by selling goods and services to the household sector. It hires the factors of production, i.e., land, labour, capital and organisation, owned by the household sector. The firm sector sells the entire output to households.
In a two-sector economy, production and sales are equal and there will be a circular flow of income and goods. The outer circle represents real flow (factors and goods) and the inner circle represents the monetary flow (factor prices and commodity prices). Real flow indicates
the factor services flow from household sector to the business sector, and goods and services flow from business sector to the household. The basic identities of the two-sector economy are: Y = C + I Where Y is Income; C is Consumption; I is investment.
Part – D Answer the following questions in one page.
35. Discuss the scope of Macro Economics.
Answer: The study of macro economics has wide scope and it covers the major areas as follows:
National Income: Measurement of national income and its composition by sectors are the basic aspects of macroeconomic analysis. The trends in National Income and its composition
provide a long term understanding of the growth process of an economy.
Inflation: Inflation refers to steady increase in general price level. Estimating the general price level by constructing various price index numbers such as Wholesale Price Index, Consumer Price Index, etc, are needed.
Business Cycle: Almost all economies face the problem of business fluctuations and business cycle. The cyclical movements (boom, recession, depression and recovery) in the economy need to be carefully studied based on aggregate economic variables.
Poverty and Unemployment: The major problems of most resource – rich nations are poverty and unemployment. This is one of the economic paradoxes. A clear understanding about the magnitude of poverty and unemployment facilitates allocation of resources and initiating
corrective measures.
Economic Growth: The growth and development of an economy and the factors determining them could be understood only through macro analysis.
Economic Policies: Macro Economics is significant for evolving suitable economic policies. Economic policies are necessary to solve the basic problems, to overcome the obstacles
and to achieve growth.
36. Illustrate the functioning of an economy based on its activities.
Economic System refers to the manner in which individuals and institutions are connected together to carry out economic activities in a particular area. It is the methodology of doing economic activities to meet the needs of the society.
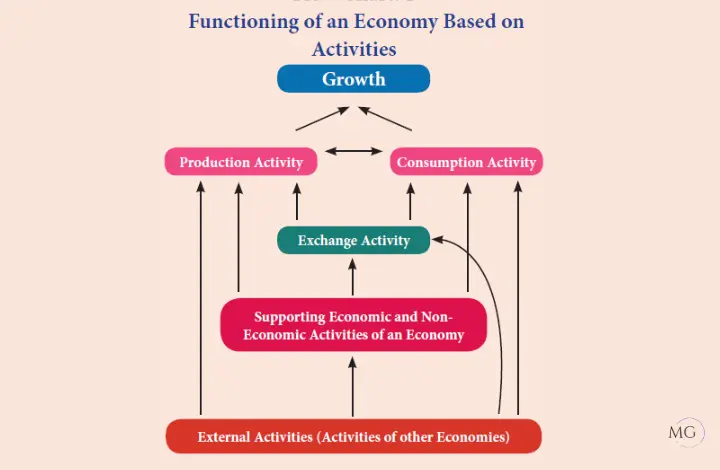
In an economy, the fundamental economic activities are production and consumption. These two activities are supported by several other activities. The ultimate aim of these activities is to achieve growth. The ‘exchange activity’ supports the production and consumption
activities.
These activities are influenced by several economic and non-economic activities. The major economic activities include transportation, banking, advertising, planning, government policy and others. The major non-economic activities are environment, health,
education, entertainment, governance, regulations etc.
In addition to these supporting activities, external activities from other economies such as import, export, international relations, emigration, immigration, foreign investment, foreign exchange earnings, etc. also influence the entire functioning of the economy.
37. Compare the features of capitalism and socialism.
Answer:
| Features | Capitalism | Socialism |
| Ownership of Means of Production | Private Ownership | Public Ownership |
| Economic Motive | Profit | Social Welfare |
| Solution of Central Problems | Free Market System | Central Planning System |
| Government Role | Internal Regulation only | Complete Involvement |
| Income Distribution | Unequal | Equal |
| Nature of Enterprise | Private Enterprise | Government Enterprise |
| Economic Freedom | Complete Freedom | Lack of Freedom |
| Major Problem | Inequality | Inefficiency |
38. Compare the feature among Capitalism, Secularism and Mixedism.
| Features | Capitalism | Socialism | Mixedism |
| Ownership of Means of Production | Private Ownership | Public Ownership | Private Ownership and Public Ownership |
| Economic Motive | Profit | Social Welfare | Social Welfare and Profit Motive |
| Solution of Central Problems | Free Market System | Central Planning System | Central Planning System and Free Market System |
| Government Role | Internal Regulation only | Complete Involvement | Limited Role |
| Income Distribution | Unequal | Equal | Less unequal |
| Nature of Enterprise | Private Enterprise | Government Enterprise | Both Private and State Enterprises |
| Economic Freedom | Complete Freedom | Lack of Freedom | Limited Freedom |
| Major Problem | Inequality | Inefficiency | Inequality and Ineffiency |
Leave a Reply